import numpy as np
import sys
class NeuralNetMLP(object):
def __init__(self, n_hidden=30, l2=0., epochs=100, eta=0.001, shuffle=True, minibatch_size=1, seed=None):
self.random = np.random.RandomState(seed)
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.l2 = l2
self.epochs = epochs
self.eta = eta
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.minibatch_size = minibatch_size
def _onehot(self, y, n_classes):
onehot = np.zeros((n_classes, y.shape[0]))
for idx, val in enumerate(y.astype(int)):
onehot[val, idx] = 1.
return onehot.T
def _sigmoid(self, z):
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-np.clip(z, -250, 250)))
def _forward(self, X):
z_h = np.dot(X, self.w_h) + self.b_h
a_h = self._sigmoid(z_h)
z_out = np.dot(a_h, self.w_out) + self.b_out
a_out = self._sigmoid(z_out)
return z_h, a_h, z_out, a_out
def _compute_cost(self, y_enc, output):
L2_term = (self.l2 *(np.sum(self.w_h ** 2.)+np.sum(self.w_out ** 2.)))
term1 = -y_enc * (np.log(output))
term2 = (1. - y_enc) * np.log(1. - output)
cost = np.sum(term1 - term2) + L2_term
return cost
def predict(self, X):
z_h, a_h, z_out, a_out = self._forward(X)
y_pred = np.argmax(z_out, axis=1)
return y_pred
def fit(self, X_train, y_train, X_valid, y_valid):
n_output = np.unique(y_train).shape[0]
n_features = X_train.shape[1]
self.b_h = np.zeros(self.n_hidden)
self.w_h = self.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=0.1, size=(n_features, self.n_hidden))
self.b_out = np.zeros(n_output)
self.w_out = self.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=0.1, size=(self.n_hidden, n_output))
epoch_strlen = len(str(self.epochs))
self.eval_ = {'cost': [], 'train_acc': [], 'valid_acc': []}
y_train_enc = self._onehot(y_train, n_output)
for i in range(self.epochs):
indices = np.arange(X_train.shape[0])
if self.shuffle:
self.random.shuffle(indices)
for start_idx in range(0, indices.shape[0] - self.minibatch_size +1, self.minibatch_size):
batch_idx = indices[start_idx:start_idx + self.minibatch_size]
z_h, a_h, z_out, a_out = self._forward(X_train[batch_idx])
delta_out = a_out - y_train_enc[batch_idx]
sigmoid_derivative_h = a_h * (1. - a_h)
delta_h = (np.dot(delta_out, self.w_out.T) *sigmoid_derivative_h)
grad_w_h = np.dot(X_train[batch_idx].T, delta_h)
grad_b_h = np.sum(delta_h, axis=0)
grad_w_out = np.dot(a_h.T, delta_out)
grad_b_out = np.sum(delta_out, axis=0)
delta_w_h = (grad_w_h + self.l2*self.w_h)
delta_b_h = grad_b_h
self.w_h -= self.eta * delta_w_h
self.b_h -= self.eta * delta_b_h
delta_w_out = (grad_w_out + self.l2*self.w_out)
delta_b_out = grad_b_out
self.w_out -= self.eta * delta_w_out
self.b_out -= self.eta * delta_b_out
z_h, a_h, z_out, a_out = self._forward(X_train)
cost = self._compute_cost(y_enc=y_train_enc, output=a_out)
y_train_pred = self.predict(X_train)
y_valid_pred = self.predict(X_valid)
train_acc = ((np.sum(y_train == y_train_pred)).astype(np.float) / X_train.shape[0])
valid_acc = ((np.sum(y_valid == y_valid_pred)).astype(np.float) / X_valid.shape[0])
sys.stderr.write('\r%0*d/%d | Cost: %.2f | Train/Valid Acc.: %.2f%%/%.2f%% ' %(epoch_strlen, i+1, self.epochs, cost, train_acc*100, valid_acc*100))
sys.stderr.flush()
self.eval_['cost'].append(cost)
self.eval_['train_acc'].append(train_acc)
self.eval_['valid_acc'].append(valid_acc)
return self
https://wikidocs.net/37406 (back propagation)
신경망 훈련
nn=NeuralNetMLP(n_hidden=100, l2=0.01, epochs=200, eta=0.0005, minibatch_size=100, shuffle=True, seed=1)
nn.fit(X_train=X_train[:55000], y_train=y_train[:55000], X_valid=X_train[55000:], y_valid=y_train[55000:])
200/200 | Cost: 5065.78 | Train/Valid Acc.: 99.28%/97.98%
Graph
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(nn.epochs), nn.eval_['cost'])
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.show()
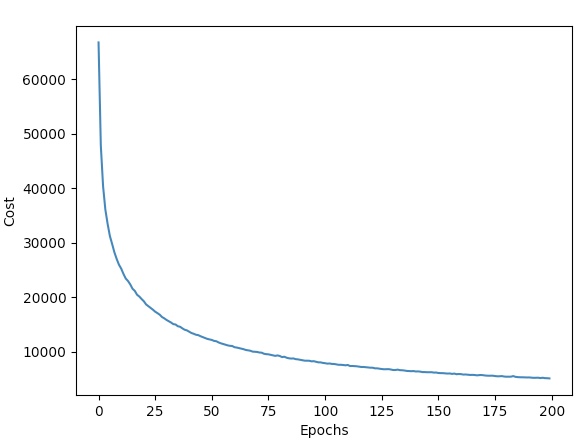
100번의 에포크 동안 비용이 많이 감소한다.
이후의 에포크에서는 천천히 수렴하는 것을 알 수 있다.
plt.plot(range(nn.epochs), nn.eval_['train_acc'], label='Training')
plt.plot(range(nn.epochs), nn.eval_['valid_acc'], label='Validatation', linestyle='--')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()

약 50번의 에포크에서 훈련 정확도와 검증 정확도가 일치하고, 이후에 네트워크는 과대적합됨을 알 수 있다.
과대 적합의 영향을 줄이기 위해서는 규제의 강도를 높여야 한다.
l2를 기존 0에서 0.1로 상승시키면 과대 적합을 줄일 수 있다.
신경망에서 과대적합을 줄이기 위해서 드롭아웃(dropout)을 사용한다.
Test accuracy
y_test_pred=nn.predict(X_test)
acc=(np.sum(y_test==y_test_pred).astype(np.float)/X_test.shape[0])
print('테스트 정확도: %.2f%%' %(acc*100))
테스트 정확도: 97.54%
위의 신경망의 하이퍼 파라미터로 은닉 유닛 개수와 규제 매개변수(파라미터)의 값, 학습률 등을 바꿀 수 있다.
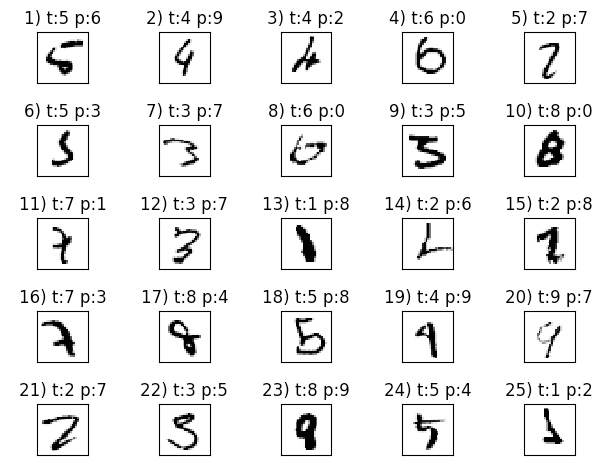
Mis_pred images
miscl_img=X_test[y_test!=y_test_pred][:25]
correct_lab=y_test[y_test!=y_test_pred][:25]
miscl_lab=y_test_pred[y_test!=y_test_pred][:25]
fig, ax=plt.subplots(nrows=5, ncols=5, sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax=ax.flatten()
for i in range(25):
img=miscl_img[i].reshape(28 ,28)
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[i].set_title('%d) t:%d p:%d' %(i+1, correct_lab[i], miscl_lab[i]))
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()